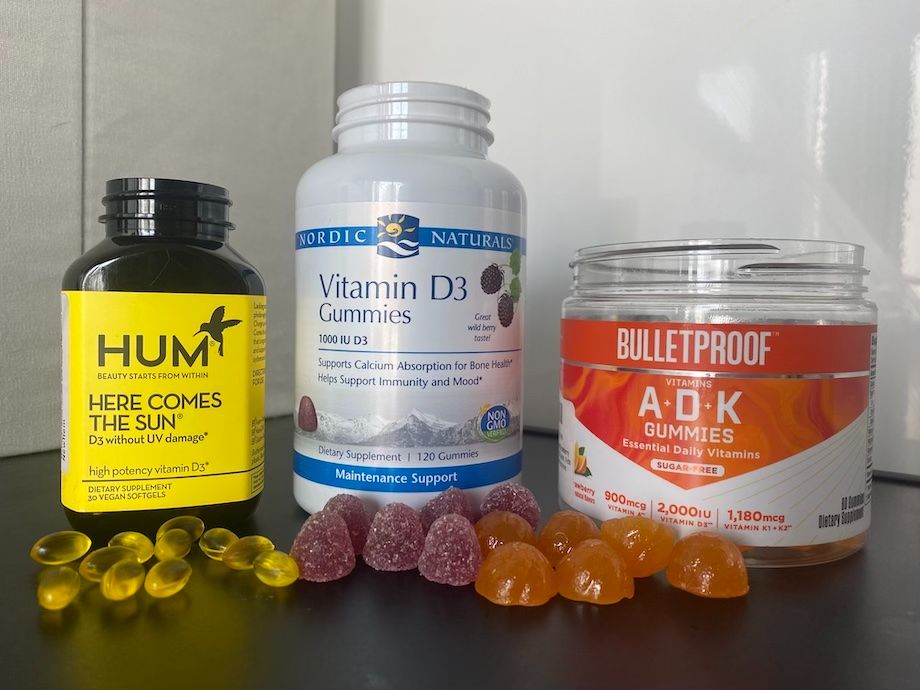
If you aren’t spending much time in the sun, you might need more vitamin D3. Fortunately, you can also get vitamin D3 from certain foods and the best vitamin D supplements to meet your intake goals. These foods are often fortified with vitamin D since there are few natural sources. While most people know vitamin D for its role in bone health, it also supports mood, immune health, and muscle function. Unsure about what vitamin D3 is? We’re here to clarify. Read on to learn about vitamin D3 benefits, vitamin D intake recommendations, and potential vitamin D side effects.
What Is Vitamin D3?
There are two main forms of vitamin D, which are vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) and vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol). Both are fat soluble vitamins, meaning they absorb better when taken with a source of fat and are stored in the body’s fat tissue. Vitamin D2 is mainly found in plant-based foods, while vitamin D3 is in animal-based foods. Vitamin D is often referred to as the “sunshine vitamin,” and vitamin D3 is the form naturally produced by the body from sun exposure to the skin. Because there are not a lot of foods that naturally contain vitamin D, both forms are commonly added to cereals, milk, and juices.
Vitamin D3 is thought to be more effective at raising blood levels of vitamin D. It has a longer half-life and stays in the body for longer than vitamin D2. It’s thought to be more bioavailable and easily absorbed. For these reasons, vitamin D3 is more commonly used in supplements to address vitamin D deficiencies.
Food sources of vitamin D3 include:
- Fatty fish (salmon, trout, tuna, sardines, mackerel)
- Egg yolk
- Beef liver
- Fortified milk
- Fortified orange juice
- Fortified cereal
- Fortified yogurt
RELATED: Best Supplements for Men
Benefits of Vitamin D3
There are several potential benefits of vitamin D3 that extend beyond bone health. Whether you’re looking to improve your mood, strengthen your immune system, or ease your bowels, vitamin D3 might help.

Helps Strengthen Bones
Vitamin D3 plays a vital role in bone health. It helps our bodies absorb calcium and phosphorus from the foods and supplements we consume. Without sufficient vitamin D3, our bodies may struggle to absorb these nutrients effectively. Calcium is the main mineral in bones and it’s essential for bone mineral density for more resilient, healthier bones. Adequate vitamin D3 ensures that calcium can be utilized to keep bones strong.
Vitamin D3 is especially important for aging adults, who are at an increased risk of developing osteoporosis. Osteoporosis is characterized by weak, brittle bones and a higher risk of fractures. Getting enough vitamin D may help prevent bone loss, a key factor in the development of osteoporosis.
RELATED: Best Protein Powder for Seniors
Can Support Immune Health
Evidence suggests that vitamin D3 may support immune function1 by influencing the epigenome of immune cells, especially monocytes. This means vitamin D3 may affect the way these cells work. Monocytes play a role in protecting the body from infections. When monocytes encounter bacteria or viruses that pose a threat to the immune system they can turn into other types of immune cells that fight infections or trigger an immune response. Vitamin D3 may influence the behavior of immune cells to fight infections and protect the immune system.
Strengthens Muscle Fibers
Mounting research implies2 that vitamin D3 could be associated with muscle regeneration following injury—including muscle fiber damage from resistance training. Vitamin D binds to the vitamin D receptor (VDR) found in muscle cells, which triggers various biological responses. Satellite cells, which help repair and strengthen damaged muscle fibers, have their activity enhanced by the presence of more VDRs. During muscle regeneration, vitamin D3 increases the amount of VDR in satellite cells, enhancing their ability to repair muscles.
RELATED: Best Recovery Protein Powder

Can Aid Mood or Depression
Those with low vitamin D levels may experience symptoms of depression or anxiety. Vitamin D helps regulate neurotransmitters3, which are the brain’s chemical messengers. Specifically, vitamin D3 supports the production and function of dopamine and serotonin, two neurotransmitters known to promote feelings of happiness. Additionally, vitamin D may reduce inflammation caused by oxidative stress, which has been linked to depression and anxiety. By reducing inflammation, vitamin D3 may help reduce symptoms of these mood disorders.
RELATED: Best Ashwagandha Supplement
May Help Manage Diabetes
Vitamin D levels might influence the onset of Type 1 diabetes. Type 1 diabetes is seen in individuals who lack insulin, the hormone that allows sugar in the blood to be taken up into cells to be converted into energy. Without insulin, these individuals can experience high blood sugar levels. Some studies have found4 that vitamin D supplementation may improve blood sugar metabolism in those with Type 1 diabetes, helping to regulate blood sugar levels better. On the contrary, there is a lack of evidence to support that vitamin D may improve blood sugar regulation in those with the more prevalent type of diabetes—Type 2 diabetes.
Can Reduce Risk of Multiple Sclerosis
Low blood levels of vitamin D may be associated with a higher risk of developing multiple sclerosis, a condition where the immune system attacks the nervous system. Vitamin D is believed to help modulate the immune system and reduce inflammation, possibly lowering the risk of multiple sclerosis. However, more research is needed to explore these potential connections.

May Help Those With Irritable Bowel Syndrome
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is marked by uncomfortable symptoms including constipation, diarrhea, gas, and abdominal pain. Vitamin D3 could help alleviate these symptoms in those with IBS. The gut microbiome, intestinal permeability, and gut immune function are thought to be involved in the development of IBS. Vitamin D3 may help improve these areas of gut health, potentially reducing IBS symptoms4.
Can Reduce Risk of Pregnancy Complications
The pregnant parent is the sole source of vitamin D for a developing baby, so the baby relies on the parent’s vitamin D levels to meet its needs. Vitamin D supplementation may help reduce pregnancy complications related to gestational diabetes and preeclampsia. Furthermore, some studies5 also suggest that low levels of vitamin D during pregnancy may increase the risk of preterm labor, but ongoing research is needed.
Helps Prevent Rickets In Babies
Rickets is a bone disease in children, usually caused by a long-term deficiency of vitamin D. It leads to weak, soft bones, which can result in delayed growth, bowed legs, and muscle weakness. Getting plenty of vitamin D in early childhood may help prevent children from developing rickets.
Additionally, most cases of rickets are curable when treated early. It’s important for breastfeeding parents to make sure they are getting enough vitamin D in their diet to support the development of normal bone growth. Pediatricians often recommend vitamin D supplements to help children meet their nutritional needs.
Adults can experience a similar condition known as osteomalacia.
RELATED: Best Protein Powder for Kids
How Much Vitamin D3 Do I Need?
If you’re a homebody, have darker skin, or live somewhere that gets less sunlight, it could be difficult to get vitamin D from sunlight exposure. Sunscreen, often worn to protect against skin cancer, can also decrease vitamin D production. The fact that not many foods contain vitamin D naturally makes intake through food a little more challenging. However, fortified foods and supplementation can help you meet your daily needs. The recommended dietary allowance (RDA)6 of daily vitamin D varies based on age.
- Children up to 12 months: 400 international units (IU)
- People ages 1 to 70: 600 IU
- People over 70: 800 IU
RELATED: Best Multivitamins for Men | Best Multivitamins for Women

Vitamin D Deficiency
A vitamin D deficiency can develop when you don’t get enough vitamin D from sunlight or your diet. Sometimes it can be due to your body not properly absorbing the nutrient. While it’s well known that insufficient vitamin D can lead to weak, brittle bones, there are other signs that may indicate a deficiency.
When bones lack the nutrients needed to stay strong, it can result in bent or deformed bones, bone pain, and joint deformities. Since vitamin D is essential for calcium absorption, a deficiency may also lead to low blood calcium levels. If left untreated, this can cause issues like muscle weakness, cramps, fatigue, and even depression.
In some cases, vitamin D deficiency may be linked to underlying medical conditions, weight loss surgery, or certain medications. If you suspect you’re not getting enough vitamin D, it’s important to consult with your healthcare provider who can run a blood test to check your levels.
Side Effects of Vitamin D3
Though rare, it is possible to get too much vitamin D from dietary supplements, leading to toxicity. However, vitamin D toxicity does not occur from excessive sun exposure. Vitamin D3 boosts calcium absorption into the bloodstream, but taking too much through supplementation can cause blood calcium levels to rise too high (hypercalcemia). This can result in symptoms such as nausea, frequent urination, increased thirst, weakness, confusion, loss of appetite, poor balance, and slurred speech.
The upper limit for vitamin D7 intake in adults is 4,000 IU per day. Exceeding this amount of vitamin D regularly can lead to side effects or potential toxicity. Older adults or individuals requiring vitamin D supplementation should consult a healthcare professional to determine a safe and appropriate dosage.
Vitamin D3 Benefits: Final Thoughts
Sunlight is the primary source of vitamin D, but many Americans don’t get enough through sun exposure alone. To potentially prevent bone loss, boost your immune system, strengthen muscle fibers, and improve your mood, consider incorporating fortified foods and a vitamin D3 supplement into your daily routine. Vitamin D3 is thought to stay in your bloodstream longer than other forms of vitamin D, possibly making it a more effective option. Most children and adults aged 1 to 70 need 600 IU of vitamin D3 daily. A high-quality multivitamin can help fill any nutrient gaps, ensuring you get enough of this essential vitamin every day.
Vitamin D3 Benefits: FAQs
Is it OK to take vitamin D3 every day?
Yes, it’s OK to take vitamin D3 daily, as it provides several important benefits for overall health. Vitamin D3 supports healthy bones by aiding in calcium and phosphate absorption, which is important for maintaining bone density. Additionally, it bolsters the immune system, helping the body fight off infections. Vitamin D3 also contributes to muscle health by enhancing muscle fiber recovery. Taking vitamin D3 daily may help strengthen bones, immunity, and muscle fibers.
What’s the difference between vitamin D2 and vitamin D3?
Unlike vitamin D2, the body makes vitamin D3 when skin is exposed to ultraviolet rays from the sun. Vitamin D2 is found in plant foods while vitamin D3 is from animal sources. Vitamin D3 is generally considered more effective than vitamin D2 at raising and maintaining vitamin D levels because it has a longer half-life in the body.
What are the signs of vitamin D3 deficiency in adults?
Signs of vitamin D3 deficiency may include bone pain, bowed bones, and joint deformities. Other signs that may indicate a vitamin D deficiency could be muscle weakness, cramps, depression, and fatigue.
Are there side effects to taking vitamin D3 supplements?
Yes, it’s possible to notice side effects from taking too much vitamin D3 through supplements. Although vitamin D toxicity is rare, those who take more than the daily upper limit (4,000 IU) may experience nausea, weakness, slurred speech, and poor balance. Consult your doctor if you’re concerned about your vitamin D3 intake.
References
- Martens, P. J., Gysemans, C., Verstuyf, A., & Mathieu, A. C. (2020). Vitamin D’s Effect on Immune Function. Nutrients, 12(5), 1248. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12051248
- Latham CM, Brightwell CR, Keeble AR, Munson BD, Thomas NT, Zagzoog AM, Fry CS and Fry JL (2021) Vitamin D Promotes Skeletal Muscle Regeneration and Mitochondrial Health. Front. Physiol. 12:660498. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.660498
- Akpınar, Ş., & Karadağ, M. G. (2022). Is Vitamin D Important in Anxiety or Depression? What Is the Truth?. Current Nutrition Reports, 11(4), 675–681. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13668-022-00441-0
- Jalili, M., Vahedi, H., Poustchi, H., & Hekmatdoost, A. (2019). Effects of Vitamin D Supplementation in Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. International Journal of Preventive Medicine, 10, 16. https://doi.org/10.4103/ijpvm.IJPVM_512_17
- Dovnik, A., & Mujezinović, F. (2018). The Association of Vitamin D Levels with Common Pregnancy Complications. Nutrients, 10(7), 867. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10070867
- National Institutes of Health (NIH). Recommended Dietary Allowances and Adequate Intakes, Vitamins. Accessed August 20, 2024.
- National Institutes of Health (NIH). Tolerable Upper Intake Levels, Vitamins. Accessed August 21, 2024.